Table of contents
- TOC
Introduction
In this session, you will complete one big exercise as a recap of everything that you have learned about RISC-V and C up to now. In Session 5, we already briefly discussed the concept of a linked list. Now, you will implement an interface with a number of operations on linked lists in C, and you will translate the C code to RISC-V code. You will start working on this implementation in the current exercise session. However, to fully complete the assignment will probably take more time than just one session. You can, if you choose, work on this interface for the rest of the semester, at your own pace. Questions can be asked in the current session, in the last session of the semester (this will also be a revision session), and on the discussion forum.
Implementing the full interface is a great way to prepare yourself for the RISC-V programming part of the exam. C programming will not be evaluated on the exam. However, you might need to translate C code to RISC-V code. Therefore, we recommend to also implement the C part. Furthermore, implementing the interface in RISC-V will be a lot easier when you have C code that you can translate, especially if you wrote that C code yourself.
Tip: A good order in which to solve this assignment is to implement a function first in C, then translate this to RISC-V, then move on to the next C function and so forth. Improving at C will help your understanding of assembly and the opposite is true as well. Having the function implementation fresh in your memory will also help your assembly implementation.
Note: We will not upload solutions for this exercise session. Instead, we provide a thorough testing suite and clear instructions on how to use it. As it is common for more complex programs, there is no single correct way of doing things. If your program passes the tests that we made, then you can assume that your program is also a good solution for the task.
Dynamic memory
Sometimes we want to use a data structure, but we do not know how big it might become before running the program. To solve this problem, we can use dynamic memory to define data structures that might grow or shrink during runtime. The space reserved for dynamic allocation of memory is called the heap. In session 5, we implemented a stack structure by using the heap. We will now use the same concepts to create a list that is not limited in size before execution, as opposed to a regular array in C.
Linked list
Simply put, a linked list is a data structure that allows to link different nodes with each other by using pointers. The assignment requires you to implement a one-directional linked list, where each node consists of a value and a pointer to the next node. For more details, see the section about data structures.
Let’s have a look at an example of how linked lists work:
-
Initalization of the list: We create an empty list where the pointer to the first element has the value
NULL.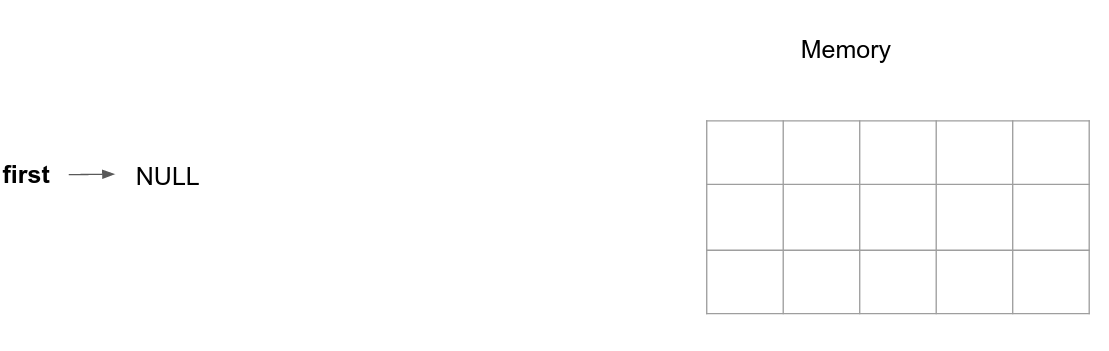
-
Adding an element to the list: We add the value
5to the linked list. We can do this by allocating some space on the heap for our new node and setting the value of thefirstpointer to the allocated memory. We can then write our value in memory and let the next pointer of the node point toNULL.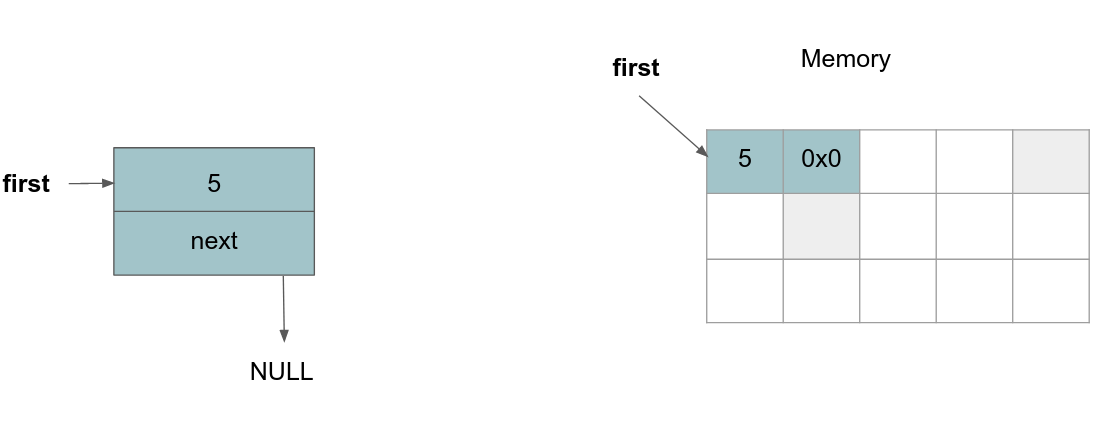
-
Adding a second node to the list: We now want to add a second node with the value
3to the list. We can do this in the same way as the previous step. Note that we want to change the value of thenextpointer of the previous node to point to our new node.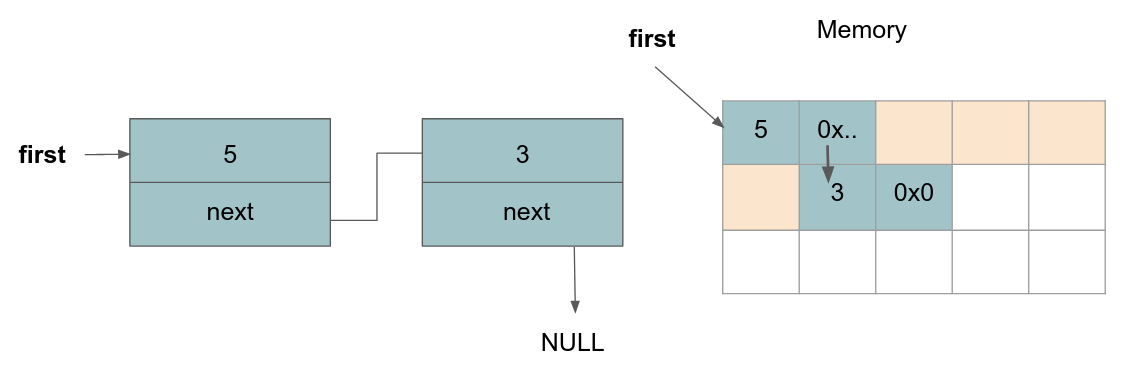
-
Removing a node: We want to delete the previously added node with value
3. To do this, we need to free the space used for the node we want to delete and make sure that thenextpointer of the node with value5is changed to have theNULLvalue, since there will be no longer a next node in the list.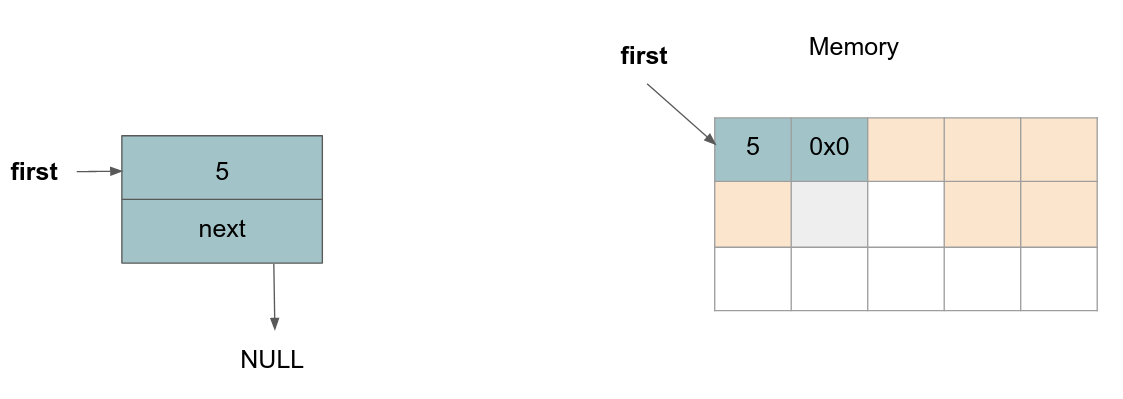
Now that you understand the basics, we can move on to the exercise.
RARS setup
Before you begin, make sure that RARS is configured correctly. Open the Settings menu in RARS and make sure that the options Assemble all files in directory and Initialize program counter to global main if defined are enabled. This will allow you to work easily with multiple files.
Linked lists interface
To get started, download linked_list.zip. Inside, you will find the following files:
-
c/linked_list.h: header file containing the definition of the interface functions. -
+
c/linked-list.c: the template in which you need to implement all function definitions. -
c/linked-list-tests.c: the C test suite. This file contains the main function that executes all tests in the suite. Look at the implementation of the different functions to get an idea of how to use the linked list interface. -
c/Makefile: File that is used to build the C project. Use the commandmakeinside the C folder to generate the test suite linked-list and run it. You can try this out immediately after downloading. It should simply fail all tests. -
asm/linked-list-tests.asm: the RISC-V test suite. Keep this file open while writing your RISC-V functions. Whenever the test suite fails a certain test, the failing assertion will be highlighted in the simulator. This can be used to quickly discover bugs in your implementation. -
asm/malloc.asm: Our ownmallocimplementation, which is our solution to the complex allocator exercise from session 4. In your implementation you are expected to usemallocandfreeto allocate memory, as you would do in C (including the error handling!). -
+
asm/main.asm: the main function that executes the test suite. It’s possible to write your own tests in this main function before executing the test suite, if you want. -
+
asm/list-*.asm: a separate file for each interface function that you need to implement. We use separate files per function because RISC-V implementations can become long, and working in a big file can be quite an annoying experience in RARS.
You should only edit the files that start with a +.
Data structures
You can use the following data structure to represent a List element:
struct List {
struct ListNode *first;
};
The element only contains a pointer to the first node of the list. Upon initialization, the value of first will be NULL since there is no node to point to.
For the nodes (elements of the list), you should use the following data structure:
struct ListNode {
int value;
struct ListNode *next;
};
The value attribute stores the content of the list element and next is a pointer to the next node in the list.
Functions
In order to make to program work, you will need to implement a number of functions. In this section you can find a description and expected operation of each function. If you are still unsure about what the behavior of the function should be, have a look at the test suite. Each function will return a status code, indicating whether an error occurred during execution.
Tip: Implement the functions in the given order. For some of the more complicated functions, you might need to use a previously written function. The test suite will check the functions in the order below and will abort if a test fails.
Tip: In assembly, you can use
mallocandfreeas defined in themalloc.asmfile. Formalloc, pass the number of words to allocate (i.e., 1 when you want to allocate 4 bytes), and forfreepass the address that should be freed.mallocwill return the address that was allocated (orNULL, indicating insufficient memory), whilefreewill return nothing.
-
struct List *list_create();
Creates a new list by allocating astruct Listand returning the address of this list. In C, you can assume thatmallocwill work correctly, but in RISC-V you should returnOUT_OF_MEMORYifmallocfails! -
status list_append(struct List *list, int value);
Appends a value to the end of an existing list by allocating a newListElementstruct and adding it to the chain. Returns eitherOK,OUT_OF_MEMORY, orUNINITIALIZED_LIST. -
int list_length(struct List *list);
Counts the number ofListItems in the list and returns the length of this list. Can returnUNINITIALIZED_LISTif the list was not initialized. -
status list_get(struct List *list, int index, int *value);
Gets the value at position index in an existing list. Stores this value at the address stored in theint *valuepointer. Returns eitherOK,INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS,UNINITIALIZED_LIST, orUNINITIALIZED_RETVAL. -
status list_print(struct List *list);
Prints all elements of the list to the console. Returns eitherOKorUNINITIALIZED_LIST. This function is not tested by the test suites. -
status list_remove_item(struct List *list, int index);
Removes the item with the provided index from the list. Returns eitherOK,INDEX OUT OF BOUND, orUNINITIALIZED_LIST. -
status list_insert(struct List *list, int index, int value);
Inserts an element with the provided value at the provided index in the list. Thus, executing with index0should insert the new element in the front of the list, and so forth. Returns eitherOK,INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS,UNINITIALIZED_LIST, orOUT_OF_MEMORY. -
status list_delete(struct List *list);
Frees all allocated memory that was used for the list (all items and the list itself). Returns eitherOKorUNINITIALIZED_LIST.
Tip: Before translating a complex function to RISC-V it might be a good idea to explicitly write down (in comments) which registers you will allocate to which variables. This makes it much easier to keep track of sometimes very hard to read RISC-V code. It might make your life a lot easier if you have to fix a bug at a later time.
Test suites and debugging
We provide an extensive test suite for both your C and RISC-V program. The tests will be run on every interface function for all kinds of edge cases. The C suite should be relatively straightforward to use. Whenever you execute your program, the test suite will test each of the interface functions. Whenever a certain part of a test fails, you will get an assertion error together with a line number in the test suite. Check out the error in the suite to figure out what your implementation did wrong.
The RISC-V suite is a little bit more complicated. It follows exactly the same structure as the C suite, thus, if you get lost, take a look at the C implementation as well. Since there is no direct way of using assertions in RISC-V, we hacked our own version in the simulator. We use macros to execute the same assertions as the ones in C. When the assertion fails, however, we throw an exception by executing lw t0, 0xdeadbeef. The exception you will see in RARS whenever an assertion fails is of the following structure:
line 131: Runtime exception at 0x004002ac:
Load address not aligned to word boundary 0xdeadbeef
While this error message means nothing for your program, the line number points you to the assertion in linked-list-tests.asm that failed for your program. By double-clicking the message, RARS will highlight this line of code in the source file. Thus, this system makes it very easy to see where the test suite fails and why. Whenever you have an exception, make sure to check both the messages and the Run I/O tab. For errors that often occur, our exception handler prints messages with hints to Run I/O tab. This will hopefully speed up your debugging process.
Error codes
All functions, except list_create, return a status code describing whether the function was executed successfully. These are the possible codes:
typedef enum {
OK = 1,
UNINITIALIZED_LIST = -1,
OUT_OF_MEMORY = -2,
INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS = -3,
UNINITIALIZED_RETVAL = -4,
} status;
-
UNINITIALIZED_LISTis returned whenever a function is called with the valueNULLfilled in as the list parameter. -
OUT_OF_MEMORYoccurs whenevermallocreturnsNULL, and thus the function failed to execute. -
INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDSoccurs in functions that ask for an index parameter when that index is invalid (e.g., has a negative value). -
UNINITIALIZED_RETVALis used whenever a function provides a return value via a parameter. Thus, the function is supplied a pointer to which to write this return value. If that pointer points toNULL, return this error code.
Partial solutions
We provide a partial solution to the first two functions (list-create and list-append). These should help you to troubleshoot minor mistakes in your code if you are stuck. If you understand these two first functions, it should not be difficult for you to also implement the remaining functions.
list_create
.eqv OK 1
.eqv UNINITIALIZED_LIST -1
.eqv OUT_OF_MEMORY -2
.eqv INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS -3
.eqv UNINITIALIZED_RETVAL -4
.text
.globl list_create
list_create:
# Back up ra on stack
addi sp, sp, -4
sw ra, (sp)
# Malloc 1 word
li a0, 1
jal malloc
# Check whether malloc failed
bnez a0, end
# Malloc failed (it is zero). Return out of memory.
li a0, OUT_OF_MEMORY
end:
# Restore ra and return
lw ra, (sp)
addi sp, sp, 4
ret
list_append
.eqv OK 1
.eqv UNINITIALIZED_LIST -1
.eqv OUT_OF_MEMORY -2
.eqv INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS -3
.eqv UNINITIALIZED_RETVAL -4
.text
.globl list_append
list_append:
# Store RA, a0 and a1 on the stack
addi sp, sp, -12
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw a0, 4(sp)
sw a1, 8(sp)
# Malloc 2 words
li a0, 2
jal malloc
# Abort if malloc failed
beqz a0, oom
# Store int in list item
lw t0, 8(sp)
sw t0, (a0)
# Make sure new item points to null
sw zero, 4(a0)
# Check whether list is empty
lw t0, 4(sp)
beqz t0, uninit_list
# Check whether first list item exists
lw t1, (t0)
beqz t1, list_zero
# First is not empty
# proceed to first list item and start looping
mv t0, t1
find_end:
# find item that points to null (last item in list)
lw t1, 4(t0) # load next item
beqz t1, end_loop # end loop if it points to null
mv t0, t1 # otherwise, move to next item
j find_end
end_loop: # t0 has end
# store pointer to item at end of list
sw a0, 4(t0) # store pointer to new item
j ok
list_zero:
#list is empty, store pointer to new item in head pointer
sw a0, (t0)
j ok
oom:
# Malloc failed, just return out of mem error.
li a0, OUT_OF_MEMORY
j end
uninit_list:
# Our list is not initialized.
# In a0 we still have the previously malloc'ed pointer.
# Free that memory and return uninitialized list error.
jal free
li a0, UNINITIALIZED_LIST
j end
ok: li a0, OK
end:
# Restore RA from stack
lw ra, (sp)
addi sp, sp, 12
ret
Additional exercises
Make sure to respect the RISC-V calling conventions in the following exercises. Write a few unit tests to validate your implementations. These questions are very similar to the ones you will receive on test 2.
Exercise 1
Create a RISC-V program that, given a linked list, swaps every number that is divisble by 3 with its right neighbour and returns the amount of swaps that have taken place. The list is traversed once, from left to right. If the last element is divisible by 3, it must be swapped with the first element of the list. The swap count must be appended to the end of the list.
Example
- Input: {1,3,7,9}
- Output: {9,7,3,1,2}
- Explanation: 3 is divisible by itself, so 3 and 7 are swapped first. 9 is also divisible by 3 and on the last index of the list, so it is swapped with the first element (1). Two swaps have taken place, so 2 is appended to the end of the list.
Print the final list and the swap count to the terminal. You may only use list_append and list_print as auxiliary functions.
Exercise 2
Write a RISC-V program that creates a new linked list by merging two lists of equal size as follows: the element at index k (with k from 0 to the end of the lists) that is the smallest of the two lists is inserted at the front of the list, the largest is inserted at the end. Print the resulting list to the terminal.
Example:
- Input: {1,2,3} and {4,1,5}
- Output: {3,1,1,4,2,5}
- Explanation: the steps are as follows: {1,4} -> {1,1,4,2} -> {3,1,1,4,2,5}, because 4 > 1, 2 > 1, 5 > 3.
Exercise 3
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. See the following figure:
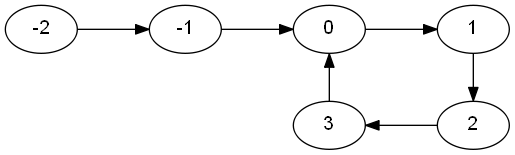
Given the head of a linked list, the C program below returns the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, it returns null. Translate the C program to RISC-V assembly. Return the position of the cycle (or -1 if there is none) in register a0, and print its value to the console.
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode *slow = head;
struct ListNode *fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
break;
}
if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}